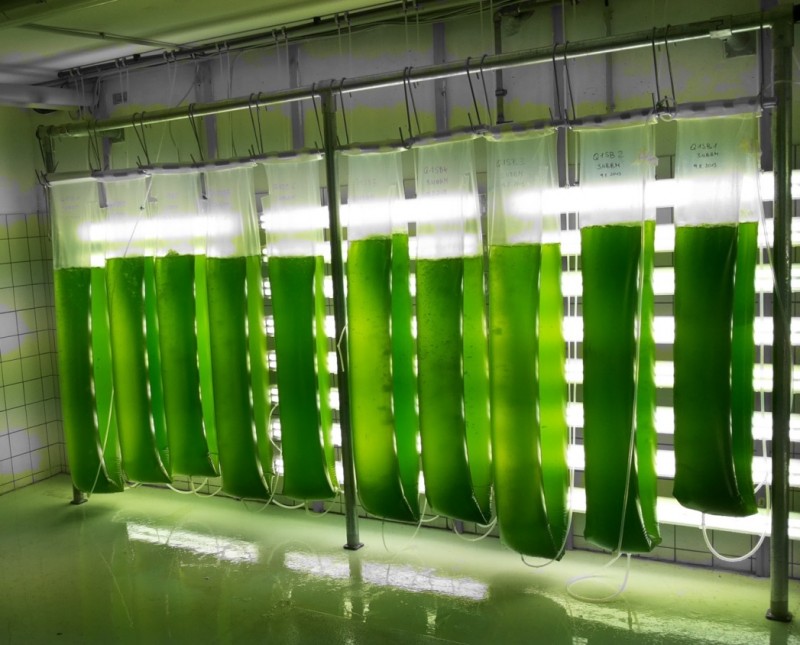
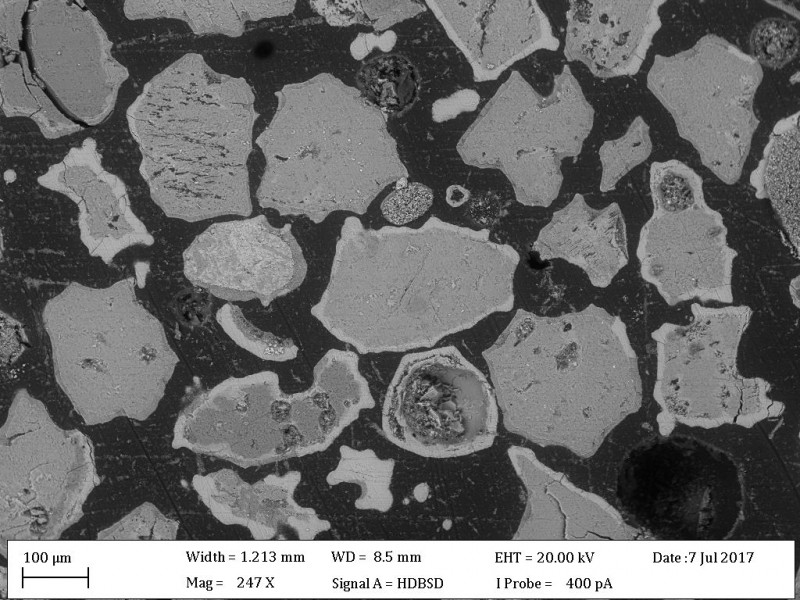
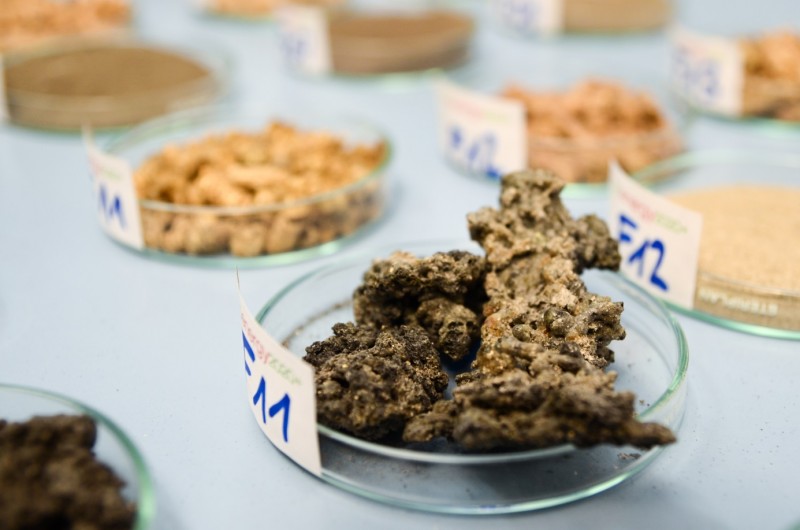
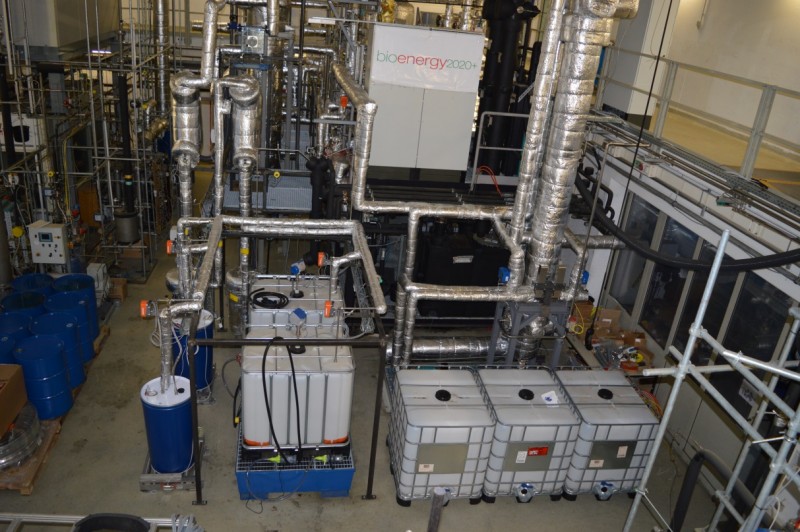
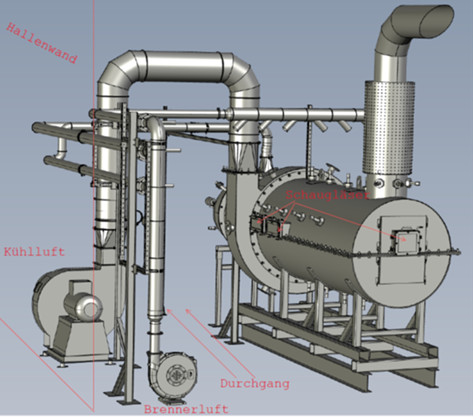
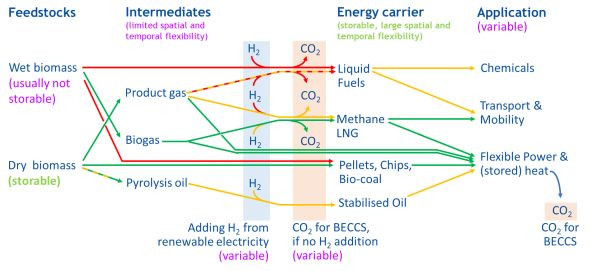
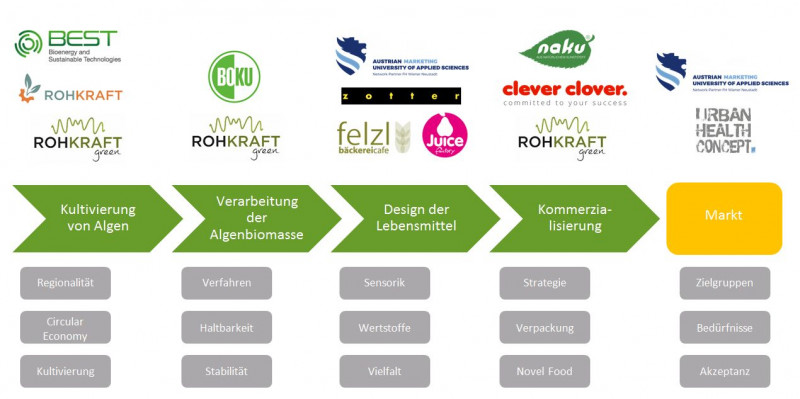
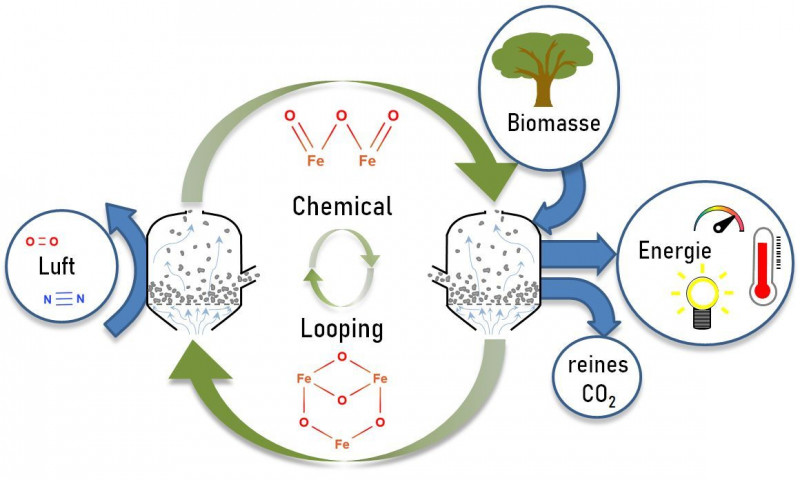
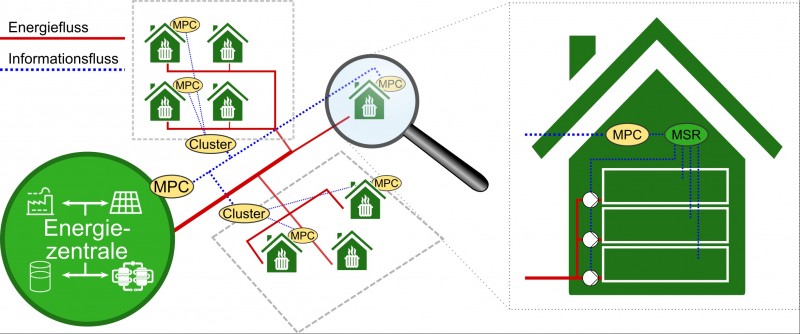
Area 1 Biorefineries
We use thermochemical, biochemical and syngas technologies for the development of biomass-, residues- and waste-based biorefineries.

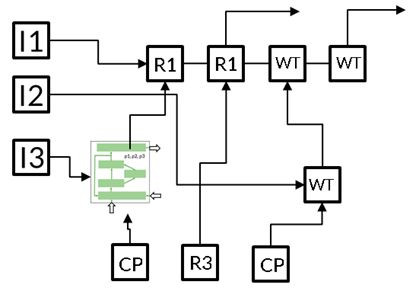
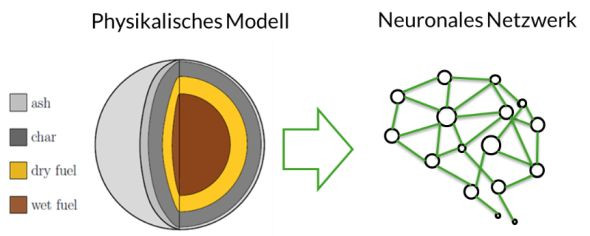
Area 2 Digital Methods and Solutions
We consistently use digital tools for technology development, technology integration into sustainable energy and resource systems and optimization of operation.

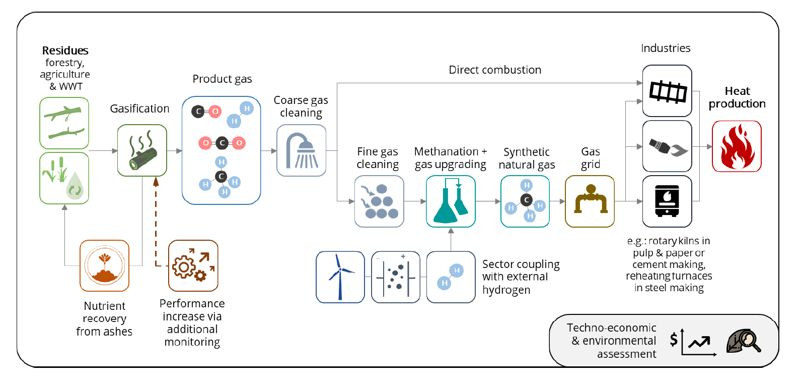
Area 3 Sustainable Supply and Value Cycles
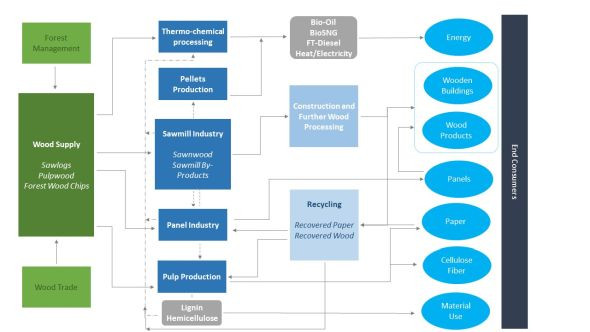
We examine the entire value cycle from the resource to the end product and its market, including recycling and energy / material recovery.
Projekte
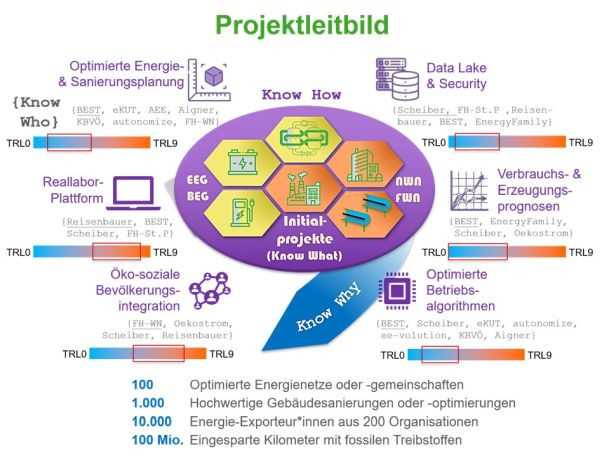
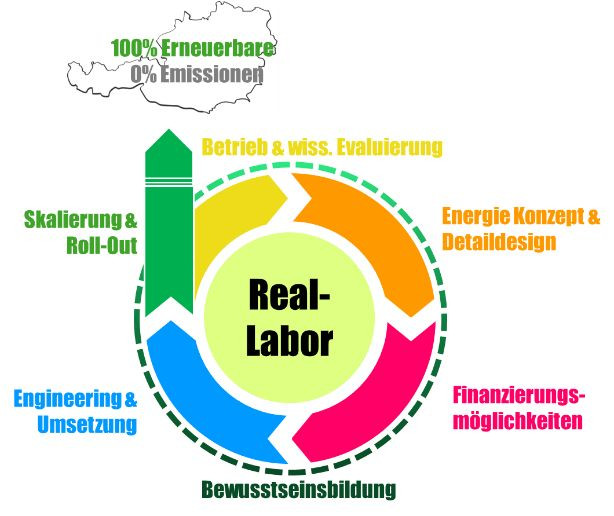
Die Initiative 100% Erneuerbare Energie Reallabore bringt Menschen aus Forschung, Entwicklung, Wirtschaft...
The decarbonisation of urban heat supply is one of the greatest challenges of the energy transition....
As part of the Green Deal, greenhouse gas emissions in the EU are to be reduced by at least 55% by 2030...
The dissertation project "RAW - Recovery of inorganic valuable materials from gas generation"...
The Interreg project ATCZ00002 - AquaCycle aims to reduce emissions in aquaculture, especially in...
Pyrolysis is a promising technology for sustainable carbon supply and waste reduction, producing solid,...
Sustainable aviation fuels (SAF) are seen as one of the key elements in reducing the aviation sector's...
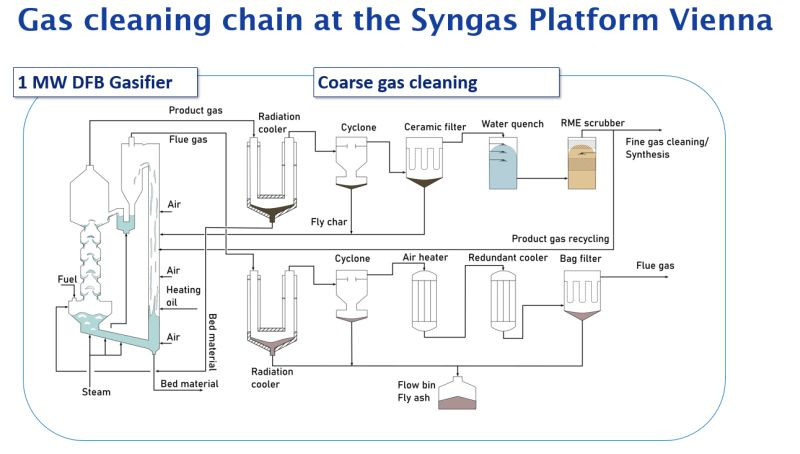
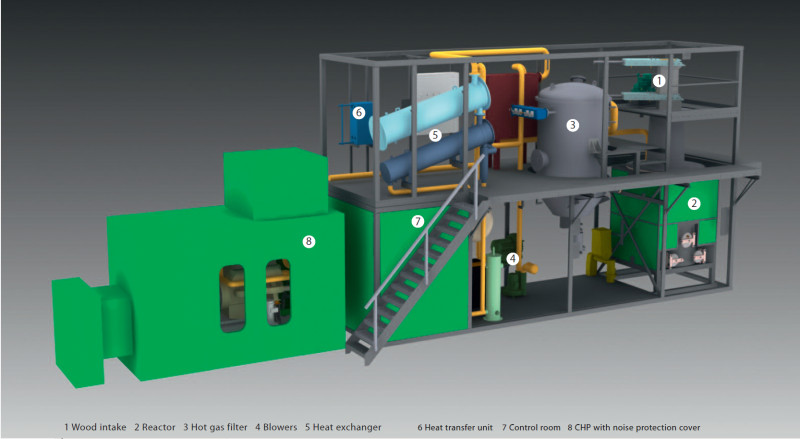
Dual fluidized bed (DFB) gasification enables the supply of renewable energy from a wide variety of residual...
Moorgebiete gehören zu den wichtigsten Kohlenstoffspeichern der Erde. Der Abbau und die Nutzung...
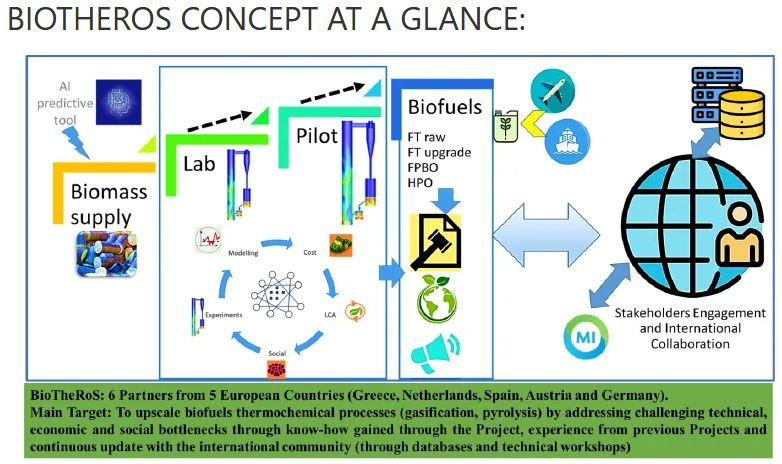
BioTheRos: Collaborative actions to bring novel BIOfuels THErmochemical ROutes into industrial Scale
Through the use of thermochemical conversion technologies, like gasification and pyrolysis, the BioTheRoS...
In order to ensure long-term sustainable biomass availability, the use of available biomass potentials...
Die Laakirchen Papier AG, ein Mitglied der Heinzel Group, produziert am Standort Laakirchen Papierprodukte...
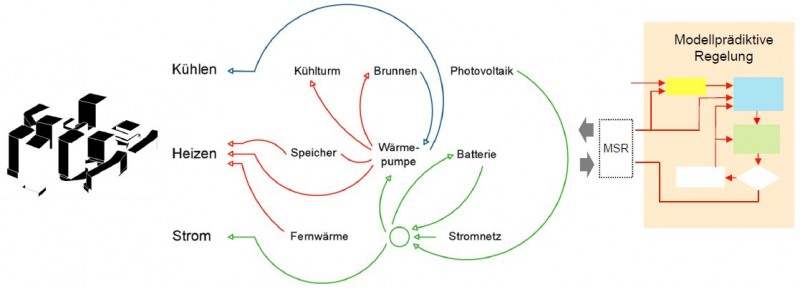
A challenge for electrical energy supply networks is maintaining the constant balance between demand...
In aquatic systems, essential biomolecules such as fatty acids are produced by phytoplankton and passed...
The ELLIPSE project will address the valorisation of two heterogeneous waste streams generated in significant...
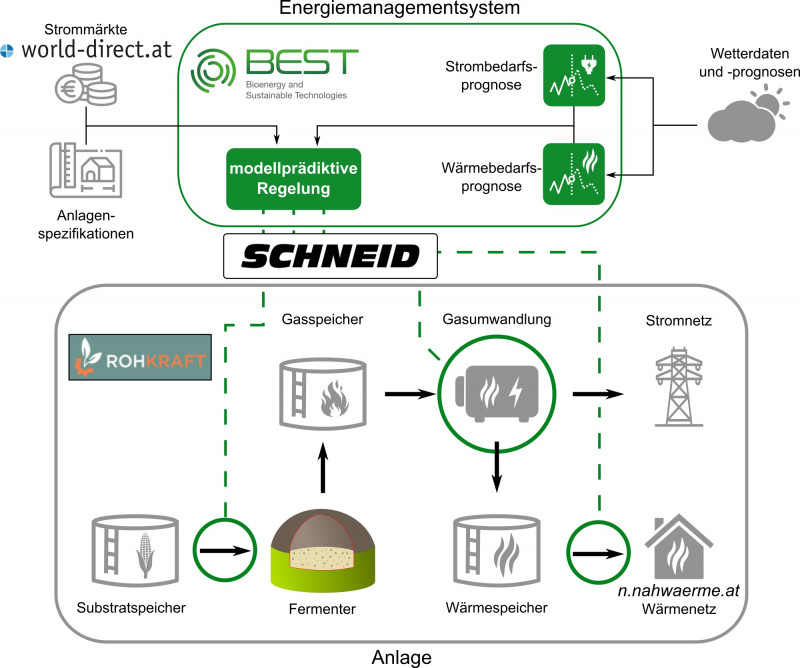
Im Rahmen des Projekts „Optimierungsbasierte ganzheitliche Energieplanung des Relax Resort Kothmühle“...
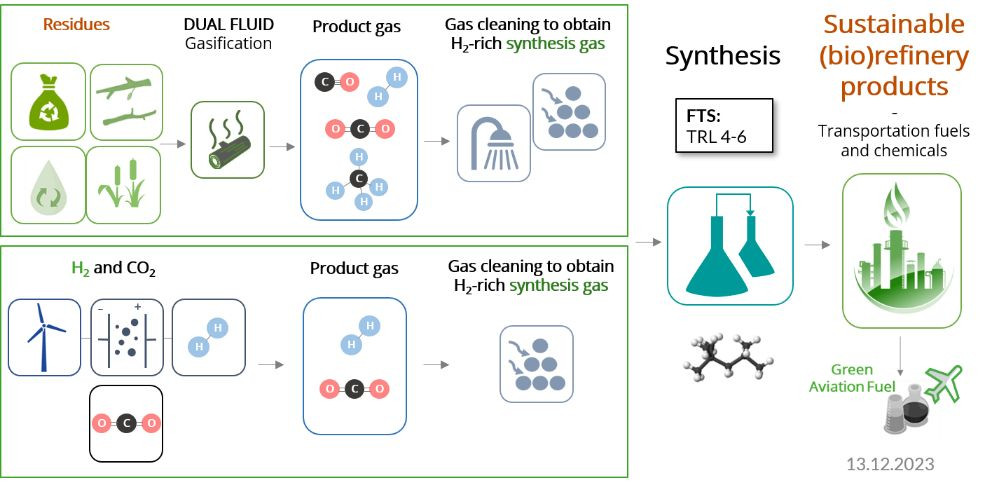
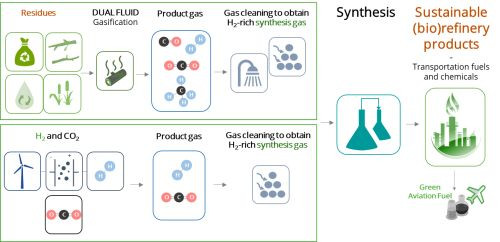
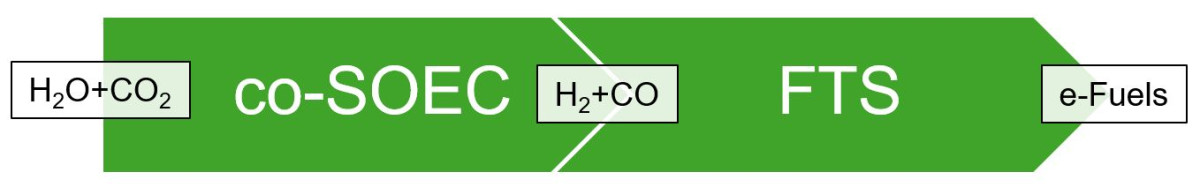
The production of synthesis gas and the downstream production of fuels and chemicals via synthesis processes...
The use of biomass or biogenic waste is increasingly shifting from purely energetic use for electricity...
Waste2Value-LevelUp! deals with the conversion of biomass residues and waste into a synthesis gas using...
The aim of the Speed-up Algorithms project is to massively accelerate the computational time of a CFD...
The project "KLAR - Sewage Sludge Inorganic Recycling" aims to make sewage sludge usable as...
Heat production in large industry sectors (steelmaking, cement production, etc.) is currently primarily...
BM Retrofit is dedicated to the development and demonstration of holistic retrofitting and...
Fossil fuels are still frequently used in food production, which is associated with significant emissions...
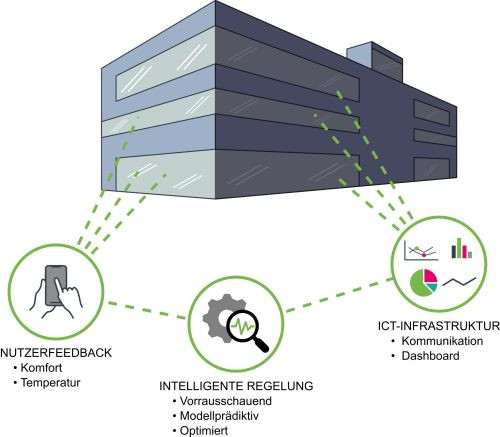
Thermal building mass activation uses building masses to condition interior spaces, but can also function...
Energy storage is of central importance in order to be able to reliably provide renewable energy, the...
Marie Sklodowska-Curie Actions depict the European flagship funding program for doctoral education and...
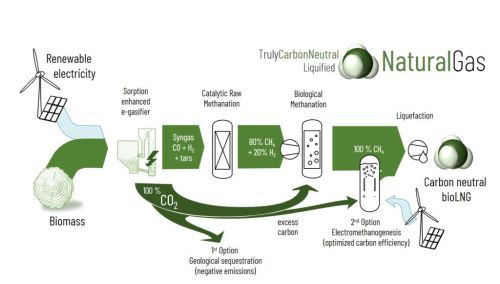
The central focus of the project CarbonNeutralLNG, coordinated by Friedrich-Alexander University Erlangen-Nürnberg,...
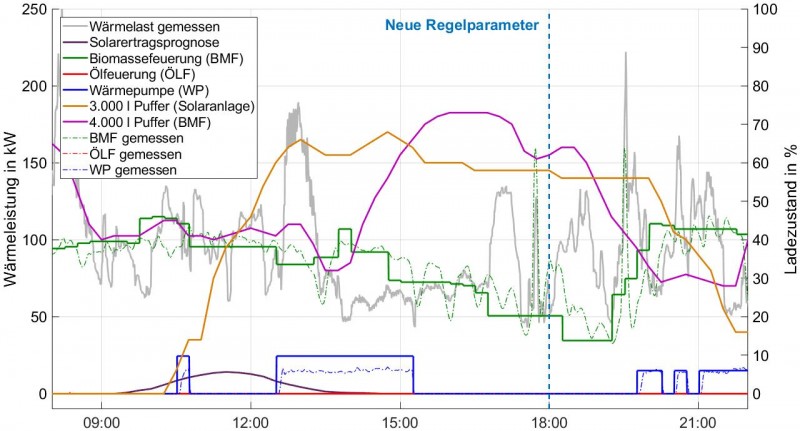
The goal of the project is to implement decentralized optimization measures for district heating (DH)...
The Alps4GreenC project, funded by INTERREG Alpine Space, aims at setting-the-scene for transnational...
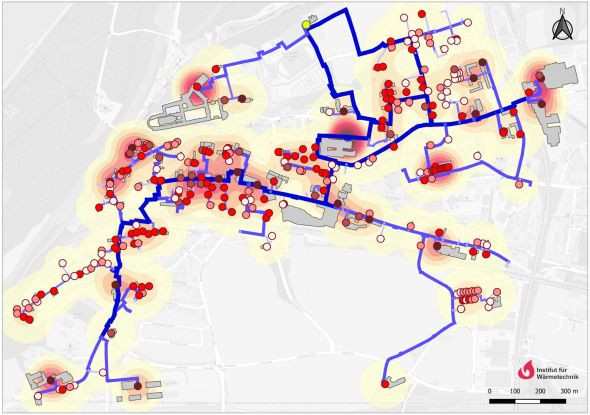
Next-generation district heating systems with a high share of renewable and volatile energy sources are...
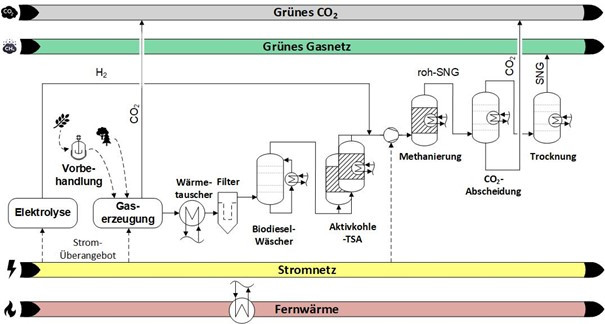
The goal of the BIG - GreenGas project is to research new processes for upgrading biogenic residues into...
In order to provide heating and cooling in the most sustainable and CO2-neutral way possible, the trend...
IEA Bioenergy Task 39: Biokraftstoffe zur Dekarbonisierung des Verkehrs (Arbeitsperiode 2022-2024) Das...
The ongoing and rapid expansion of wind and photovoltaic power generation is an undisputed principle...
The Austrian Renewable Energy Expansion Act (Erneuerbaren-Ausbau-Gesetz) envisages a significant increase...
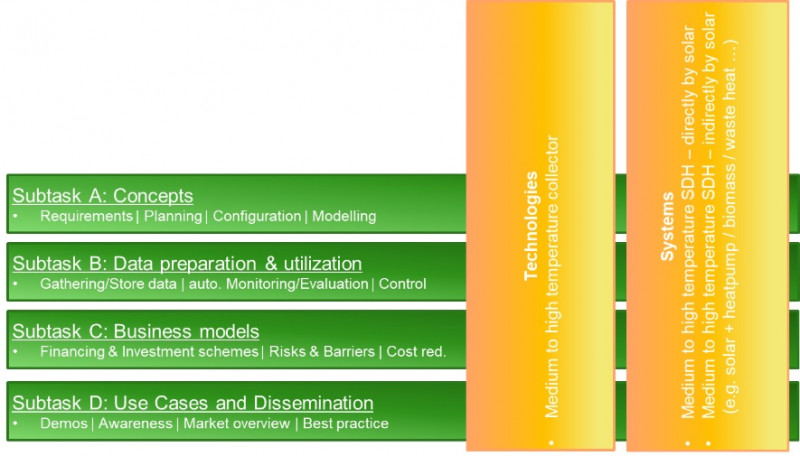
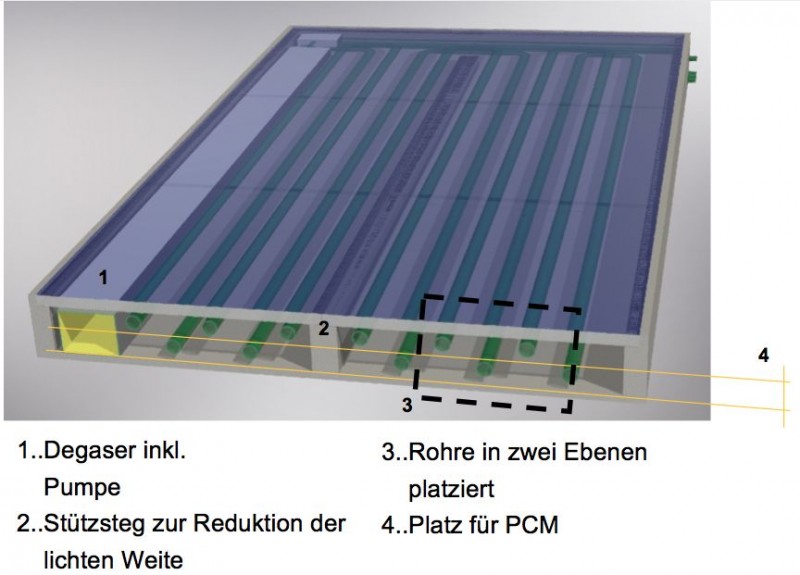
The TCP SHC has set itself the goal that solar energy technologies will cover more than 50 % of the heating...
Batteries are a key technology to enable the extensive utilization of renewable energies in the future....
In the REal project, a holistic, scalable and user-friendly concept is created. Thereby sector-coupled,...
Unterstützt von:
The main objective of the IEA AMF Task: Sustainable Aviation Fuels (SAF) is to identify the main challenges...
The IEA DHC Annex TS5 focuses on the integration of renewable energy sources into existing district heating...
The project goal is a standardized and easy-to-implement procedure for the communication, monitoring...
The CO2 intensity in the Austrian industry and energy sector can be reduced by the promising approach...
The HyStore project examines alternative technologies for hydrogen storage. Currently, hydrogen is mainly...
Climate protection requires a massive reduction in greenhouse gas emissions from existing buildings....
In 2017, the EU Winter Package laid the foundations for discussions on energy communities, which resulted...
A research project of the Technikum Wien GmbH, ENFOS e. U., AEE INTEC and BEST GmbH on behalf of the...
Das Ernährungsbewusstsein hat sich in den letzten Jahren stark verändert. Es treten vermehrt...
In order to facilitate the energy transition, the civil society should be involved and agree on measures...
Recent findings indicate that electro-fermentation provides an efficient tool to influence bacterial...
Establishing a sustainable energy and economic system and dealing with the opportunities and risks of...
Success Stories Hydrogen from solid biogenic residues Models for the future The right material...
BEST has been quite active in terms of equality and can also present some major achievements. The number...
The Interreg-project ATCZ221 – Algae4Fish aims at the utilization of agro-industrial residues as...
Starting point / motivation In the efforts to make urban energy systems more environmentally friendly...
Die Gasreinigung stellt einen großen Unsicherheitsfaktor in Vergasungsprozessen dar. Wenn...
BEST - Bioenergy and Sustainable Technologies GmbH, will establish parts of the municipality of Mureck...
The transition towards a bioeconomy will rely to a large extent on the advancement in technology of a...
Wir brennen für saubere Luft Die Verbrennung von Biomasse trägt immer noch deutlich zur...
Synopsis: In the last 10 years R&D was focused on the utilization of FT products for the production...
Construction and start-up of a new pilot plant in Vienna, Austria, which will demonstrate the conversion...
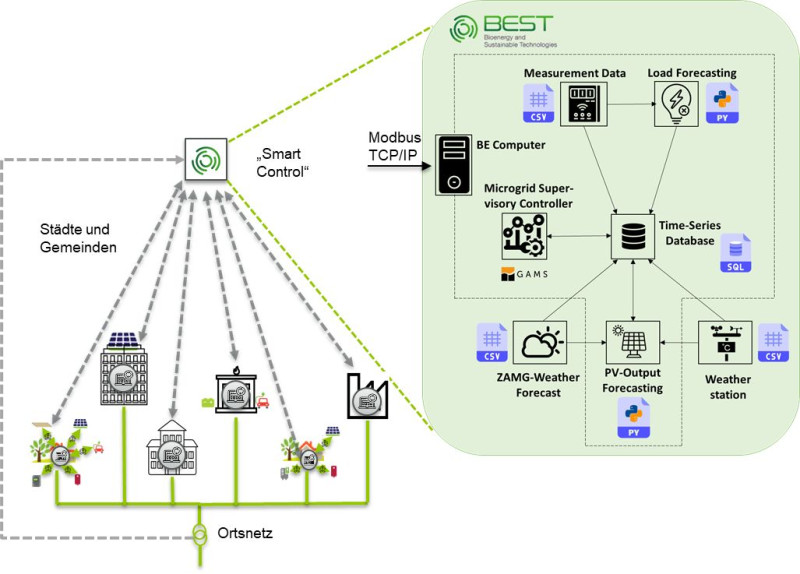
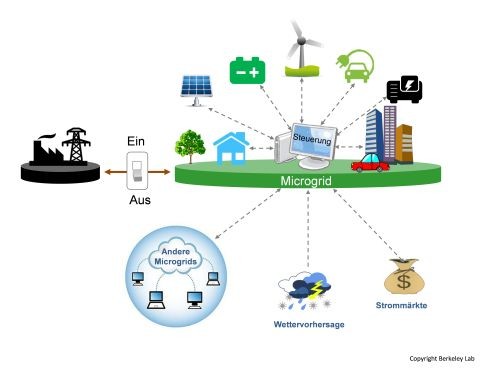
The "Microgrid Lab Wieselburg" investigates the design and operation of microgrid technologies...
More flexibility for more renewables in district heating networks - the lead project "ThermaFLEX". Starting...
The "Clean Energy for Tourism" project, which will run until the end of 2022, aims to find...
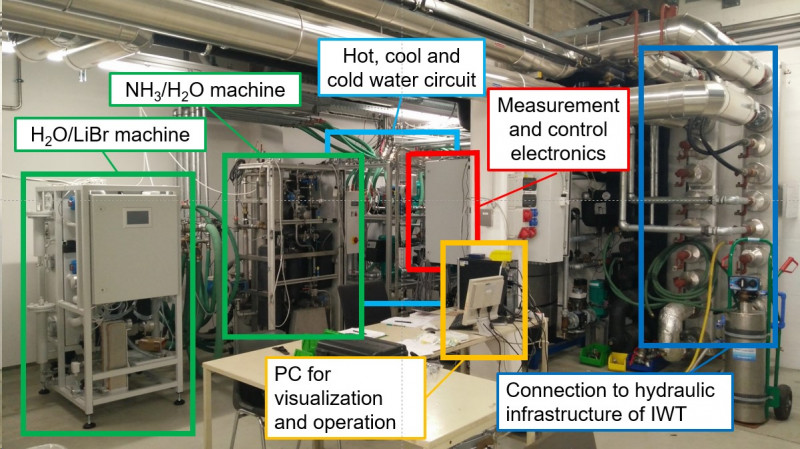
Absorption heat pumping systems (AHPS, comprising heat pumps and chillers) use thermal instead of mechanical...
Meat processing companies generate large amounts of waste that require complex and costly treatment based...
SHIP2FAIR (Solar Heat for Industrial Process towards Food and Agro Industries commitment in Renewables)...
The project “EvEmBi – Evaluation and reduction of methane emission from different biogas...
Synopsis: Fischer-Tropsch (FT) synthesis is capable to convert renewable syngas (CO and H2) to hydrocarbons...
BEST – Bioenergy and Sustainable Technologies GmbH is a technological pioneer in the field of control...
Synopsis: Heat-to-Fuel is a Horizon 2020 EU-funded project carried out by 14 partners from across...
BIOENERGY 2020+ publishes the bulletin Biobased Future, which is financed by the Austrian Ministry for...
Der derzeitige Markt für Spezial-Kunststoffprodukte wie z.B. wasserlösliche oder biologisch...
Funded by the EU, the project BRISK II aims to improve the success and usage of biomass and biogenic...
The Austrian scientific project „ Optimization of Heating, Electricity, and Cooling Services in...
Due to increased efforts to reduce CO2 emissions, the utilization of biomass for energy purposes has...
By anaerobic digestion of organic residuals and wastes high amounts of digestate and sludge arise. The...
Starting point/motivation In future city districts, the focus on a reasonable combination of different,...
The overall objective of ENERGY BARGE is to foster sustainable usage of biomass for energy production...
In the last years the research on algae cultivation as well as algae production for food and feed additives,...
Some traffic and parking areas in the urban environment are only used during limited periods. This is...
The project investigated the interaction between K-feldspar, a type of alternative bed material, and...
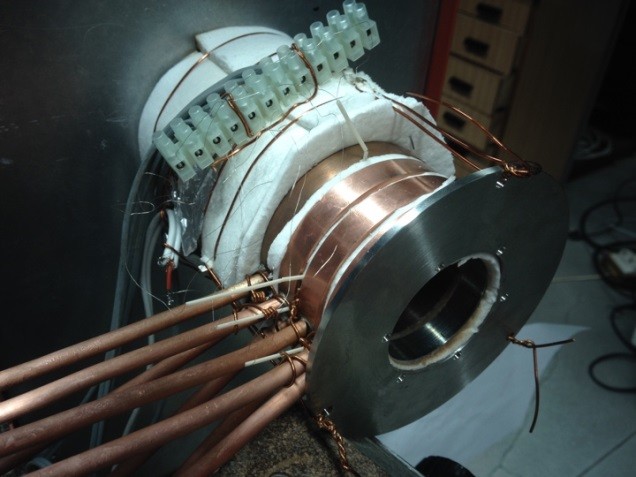
For the operation of pellet heating systems (boilers, furnaces) electrical energy for fuel transportation,...
Wood pellets may release various component during transportation and storage. Thus, relatively high concentrations...
Waste wood combustion provides economic advantages compared to the use of virgin biomass fuels but also...
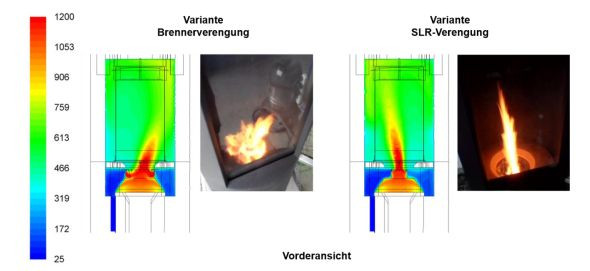
Pellet and log wood stoves are still very popular. However, these have the disadvantage that they are...
Flexibly adjustable grate systems are major prerequisites for combustion systems that can be operated...
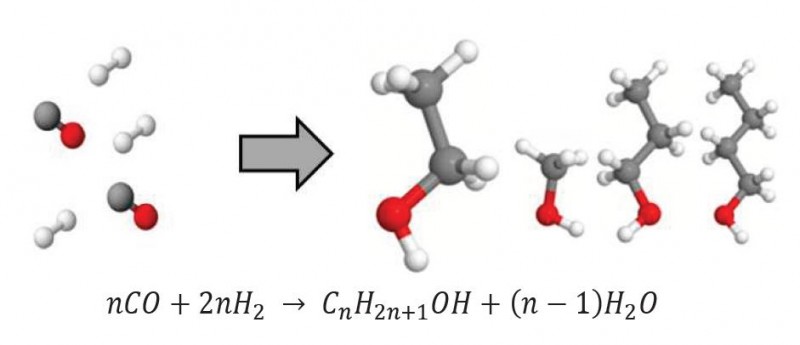
In BIOENERGY 2020+ research and development on the synthesis of mixed alcohols is done since 2010. Within...
ROMEO is a European Research and Innovation Project funded by the European Commission. It is developing...
Plants based on dual fluidized bed (DFB) gasification are a season- and weather-independent, sustainable...
In today's biomass furnaces, problematic biomass fuels such as agricultural fuels (e.g. straw), waste...
The objective of the COMET project "Barrel / day Fischer Tropsch" is the planning, construction...
Heat grids are an excellent way to integrate renewable energy sources into a universal heat supply system...
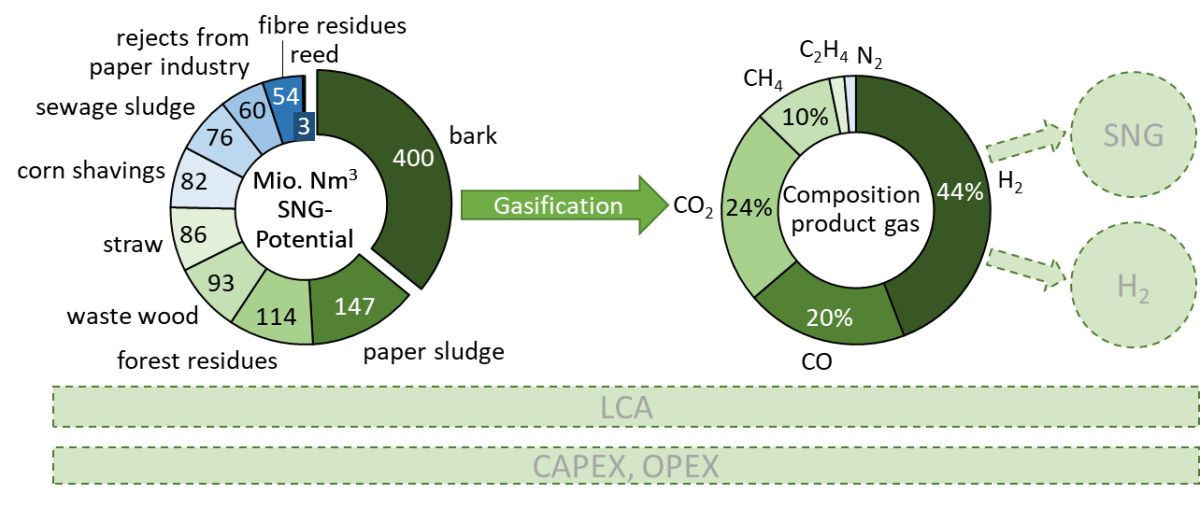
The overall objective is the upgrading of forest residues, residues of the wood processing industry and...
Die Energieversorgung der Zukunft wird zu einem großen Teil von erneuerbaren Quellen abhängen....
Steam gasification of biomass offers a great potential for polygeneration concepts, which aim at the...
Highlights
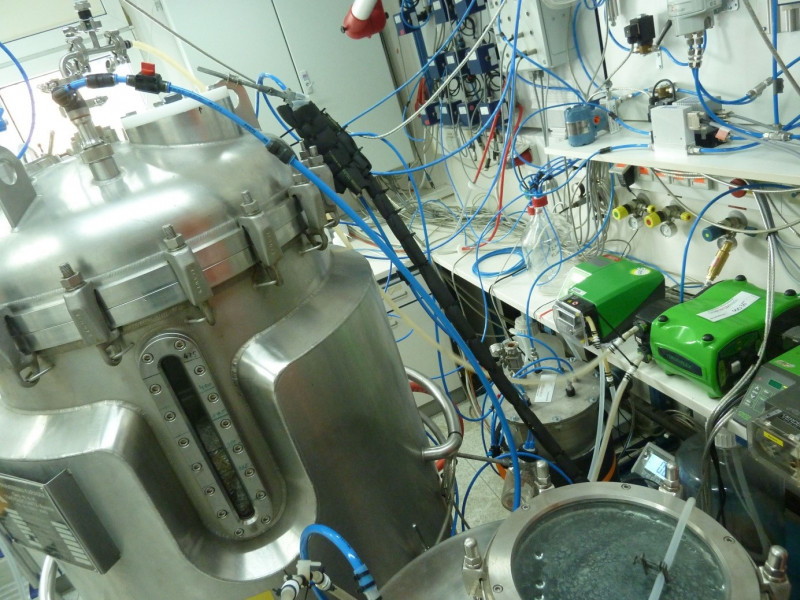
The 1 MW two-bed fluidized bed steam gas generator from bEST was ranked number one among Austrian research infrastructures in 2024.
On February 3, 2025, we launched Europe's first hydrogen valley focused on industrial applications in Styria, Upper Austria, and Carinthia.